In today’s greenhouse industry, one thing is certain: success no longer depends solely on the green thumb of the grower. Instead, it is increasingly driven by smart, data-based decisions. With shifting weather patterns, rising costs, and growing demand for year-round production, greenhouse climate optimization has become more important than ever. Understanding the local climate is now a critical step toward achieving consistent, efficient crop production.
To maximize Crop Growth and Efficiency, optimized climate and light recommendations help growers fine-tune light exposure for better yields, quality, and energy efficiency because;
- Support Optimal Photosynthesis
-Light drives growth, flowering, and fruiting. Tailored advice ensures crops get what they need.
- Improving Yield Quality & Consistency
-Stable light levels result in uniform, high-quality crops thqt meet market demands.
- Efficient Use of Resources
-Optimized lighting cuts energy waste while boosting productivity- balancing natural and artificial light use.
- Seasonal Light Adjustments
-Light varies year-round. Historical Data helps adjust lighting and shading strategies for steady performance.
Optimized Light= Stronger Crops & Higher Efficiency
With data driven light strategies, growers can boost yield, improve quality, and reduce costs thus maximizing greenhouse performance.
Weather Conditions Understanding the External Climate for Effective Greenhouse Climate Optimization
Optimizing Light & Temperature Control
– More clear days? Add Shading. More Overcast Days? Use supplemental Lighting. This helps in fine-tuning your climate strategy.
Efficient Water Management
-rainy periods reduce irrigation needs; dry spells require more water. Weather pattern guide smart water use!
Enhances Disease Prevention
-humid, cloudy weather raises fungal disease risks. Anticipate and adjust ventilation and treatment accordingly.
Improving Energy Efficiency
– Matching climate systems with weather trends cuts energy waste and ensures optimal growing conditions.
Long term weather insights help anticipate seasonal changes, refine climate control, and lower costs= healthy and happy crops and more efficient production.
Outside Temperature Managing Climate for Stable Crop Growth and Greenhouse Climate Optimization
- Maintaining Ideal Growth Conditions
-tracking averages and extremes helps you adjust ventilation, shading, and heating to stabilize the climate - Adapting to Seasonal Changes & Extremes
-helps you anticipate and manage cold snaps, heat waves, and seasonal shifts - Efficient Energy & Climate Management
-real temperature trends support smarter heating and cooling decisions, saving energy while protecting crops. - Boosting Crop Resilience
-the ability to prepare for stress events and protect yield and quality from climate fluctuations.
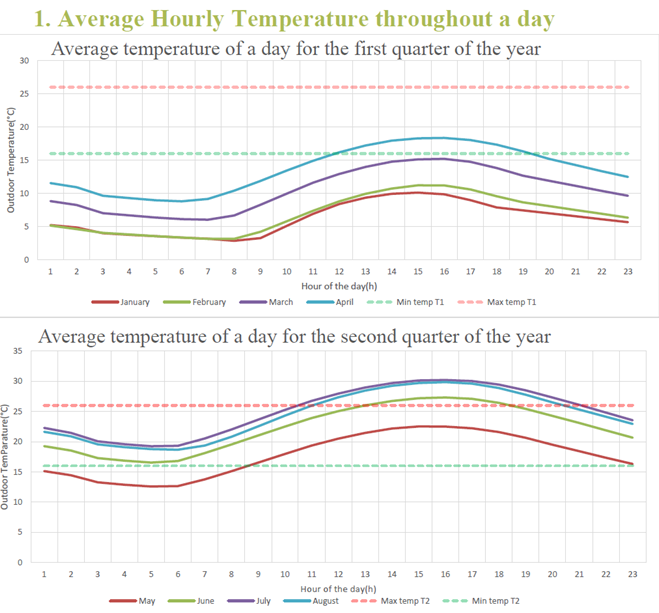

By analysing average and extreme temperatures, growers can maintain stable conditions, cut energy use, and strengthen crop resilience through effective greenhouse climate optimization for healthy, high-yielding productions.
Relative Humidity Managing Moisture for a Stable Environment and Greenhouse Climate Optimizatiion
- Maintaining Ideal Humidity Levels
-outside humidity affects transpiration and climate stability. Adjust ventilation, heating, or dehumidification to stay within the ideal range. - Protecting against Diseases and Pest
-High Humidity = Mold and Pests. By monitoring, helps manage internal humidity and prevent outbreaks. - Improving Resource Efficiency
-responding to outside humidity avoids overuse of energy for climate control, lowering costs! - Adapting to Seasonal Changes
-humidity varies year-round. Accurate data helps tailor your climate strategy for stable, consistent crop performance.

Tracking external humidity helps growers maintain ideal conditions, prevent disease, and reduce energy use — all contributing to effective greenhouse climate optimization for healthier crops and more efficient production.
Solar Radiation Understanding Solar Radiation for Smarter Greenhouse Management and Climate Optimization
Solar Radiation affects light levels and temperatures inside the greenhouse
- Optimizing Light Management
-knowing when solar radiation peals allow you to fine-tune shading screens and supplemental lightning to maintain optimal light balance for crop growth - Better Temperature Control
-By identifying high-radiation periods, the ability to adjust the ventilation, cooling, and shading to prevent heat stress and maintain an active growing climate. - Reducing Energy Costs
-using natural light reduces the need for artificial lighting and lowers energy consumption by making the greenhouse more cost-effectives, l - Anticipating Low-Light Conditions
-Maximum radiation on the darkest day helps prevent worst case scenarios. If natural light levels are insufficient, the ability to proactively adjust lighting strategies to maintain growth.
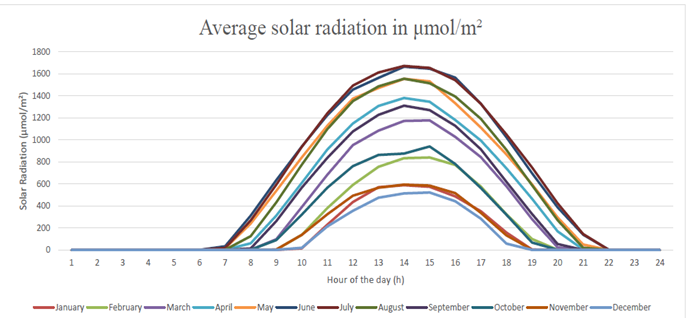
By leveraging historical data, meaning having the ability to make informed decisions that improve light management, optimize energy use, and maintain a stable climate—stronger, healthier crops and higher yields.
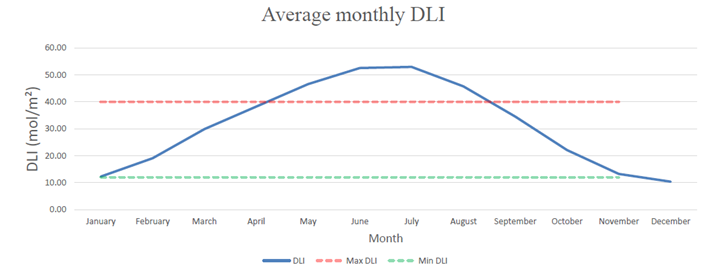
DLI Daily Light Integral and Its Role in Greenhouse Climate Optimization
DLI exceed crop requirements, leading to heat stress, water loss, and inefficient photosynthesis. On the other hand, in winter, DLI declines its optimal growth leading to slow progress of growth, heating, and lighting strategies.
Wind Direction Optimizing Ventilation and Structural Protection for Greenhouse Climate Optimization
- Designing Optimal Ventilation
-wind direction influences air movement, Co2 levels, and humidity. Knowing the patterns helps position vents and optimize airflow, reducing energy use. - Enhancing Temperature Management
-External airflow impacts internal temperatures. Helps fine tuning heating and cooling for a stable, crop friendly climate - Protecting Against Wind Exposure
-Some greenhouse sides face more wind stress. By tracking, help reinforce vulnerable areas. - Adapting to Seasonal Changes
-wind patterns vary seasonally, anticipating these changes supports year end round climate control and ventilation planning.
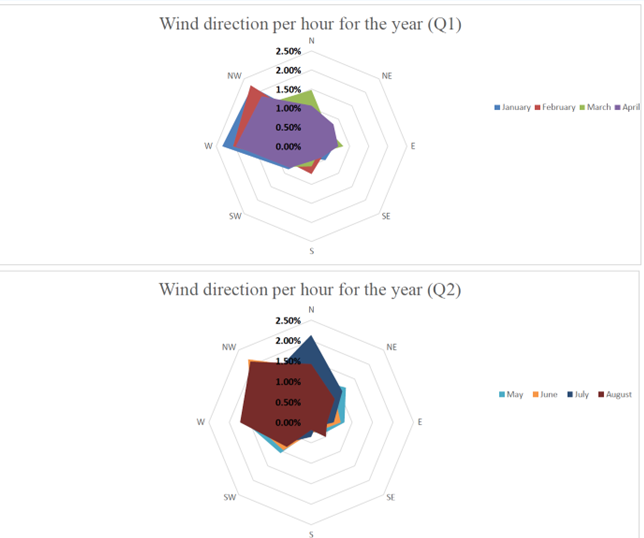
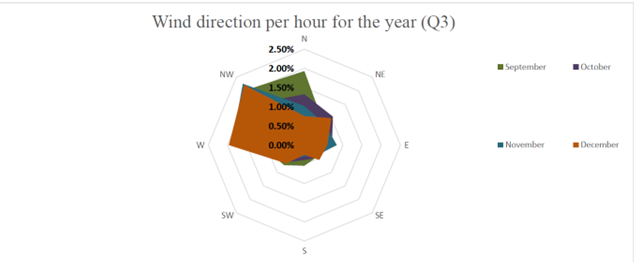
By monitoring wind direction trends, growers can improve airflow, lower energy costs, and better protetcion for the crops. Ensuring a stable and efficient greenhouse operation.
Wind Speed Protecting Your Greenhouse and Enhancing Greenhouse Climate Optimization
- Protecting Structural Integrity
-high winds can damage greenhouses. The data helps you reinforce structures and prepare for extreme weather - Enhancing Ventilation Efficiency
-wind influences air exchange and cooling. Knowing the patterns allows for smarter vent placement and airflow control - Maintaining Temperature Stability
Wind affects heat loss. Tracking trends help fine tune heating and cooling for consistent crop conditions - Adapting to Seasonal Wind Changes
-seasonal and shifts require different strategies. Data helps adapt protection and ventilation year-round.
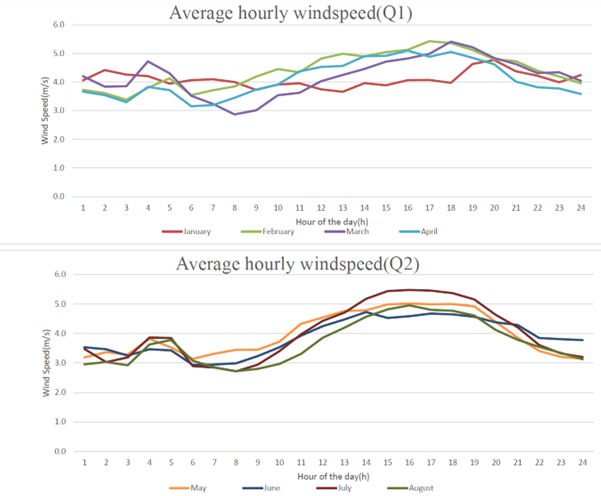
With wind inisghts, growers can strengthen structures, optimize airflow, and maintain a stable climate. This improves crop protection and energy efficiency.
